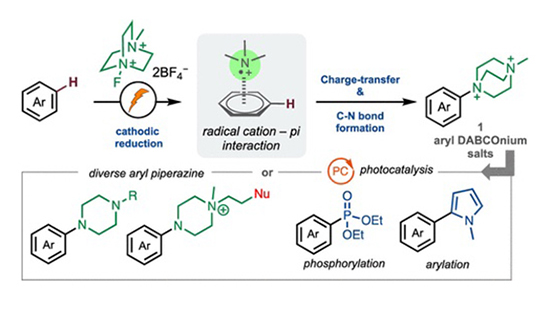
The research reveals the discovery and development of a highly selective aromatic C–H amination reaction. This electrochemical strategy employs a cathodic reduction process generating highly electrophilic dicationic N-centered radicals. These radicals efficiently participate in aromatic C–H functionalization, directing the regioselectivity of the aromatic substitution. The nitrogen-radical cation–pi interaction with arenes observed in nature facilitates a charge transfer mechanism, leading to subsequent aromatic C–N bond formation. The electrochemical process yields aryl DABCOnium salts with excellent yields and regioselectivities, covering a broad scope of arenes and accommodating various functionalities. The synthetic utility of aryl DABCOnium salt adducts is demonstrated, providing direct access to diverse aryl piperazines and enabling chemoselective cleavage for valuable aryl radicals participating in C–C and C–P bond formation via photoredox catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 146, 6 (2024)
|
|
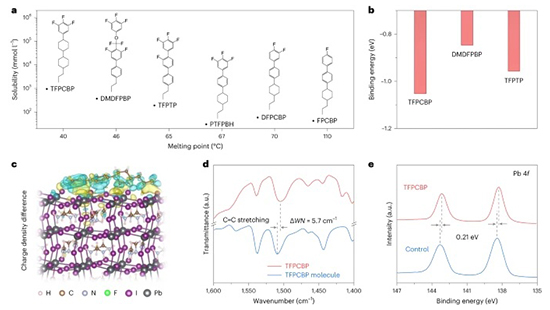
Perovskite solar cells have made strides in performance, but challenges persist in maintaining efficiency during scaling. Common additives used for large-area perovskite films can aggregate at interfaces, leading to defects and spatial irregularities. To address this, they establish design criteria for additives, preventing their problematic precipitation and ensuring uniform defect passivation. Utilizing thermotropic liquid crystals, like 3,4,5-trifluoro-4'-(trans-4-propylcyclohexyl)biphenyl, we achieve large-area perovskite films that are uniform, low in defects, and stable against environmental stress. Our modules demonstrate a certified stabilized efficiency of 21.1%, enhanced stability under damp-heat conditions, and resilience to reverse bias with and without bypass diodes. Nat Energy (2024) |
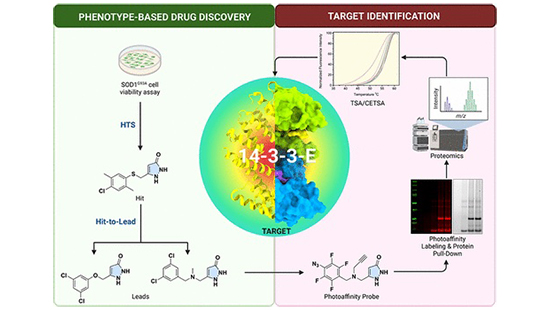
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is an incurable and fatal neurodegenerative disease. This research focused on finding small molecules to combat protein aggregation triggered by a mutation in the superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) gene, linked to 25% of familial ALS cases. After a thorough screening process, we developed three highly effective compounds against mutant SOD1 ALS. Through advanced techniques like photoaffinity labeling and proteomic analysis, we identified that two of these compounds interact with 14-3-3-E and 14-3-3-Q isoforms, known for chaperone activity. This breakthrough enhances our understanding of ALS treatment by targeting protein aggregation, paving the way for more effective therapeutic molecules. ACS Cent. Sci., 10, 1 (2024)
|



