|
Product analogue binding identifies the copper active site of particulate methane monooxygenase (Rosenzweig/Hoffman)
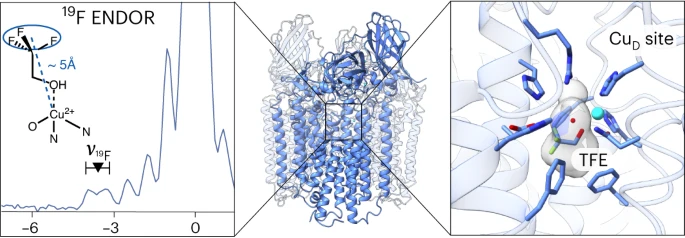 This study delves into nature’s methane-converting enzyme, particulate methane monooxygenase (pMMO). Copper is crucial for pMMO’s function, but pinpointing its active site among CuB, CuC, and CuD sites is challenging. pMMO's structure in lipid nanodiscs was successfully stabilized. Using a product analogue, 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol, as an active-site probe, advanced techniques like pulsed electron nuclear double resonance spectroscopy and cryo-electron microscopy assisted in characterization. Results indicate interactions between 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol and the CuD site, suggesting it, along with its hydrophobic pocket, is likely where methane oxidation occurs. This study showcases a robust approach to decipher metalloenzyme cryo-electron microscopy maps. Nat Catal (2023) This study delves into nature’s methane-converting enzyme, particulate methane monooxygenase (pMMO). Copper is crucial for pMMO’s function, but pinpointing its active site among CuB, CuC, and CuD sites is challenging. pMMO's structure in lipid nanodiscs was successfully stabilized. Using a product analogue, 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol, as an active-site probe, advanced techniques like pulsed electron nuclear double resonance spectroscopy and cryo-electron microscopy assisted in characterization. Results indicate interactions between 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol and the CuD site, suggesting it, along with its hydrophobic pocket, is likely where methane oxidation occurs. This study showcases a robust approach to decipher metalloenzyme cryo-electron microscopy maps. Nat Catal (2023)
|
|
Precision Proteoform Design for 4R Tau Isoform Selective Templated Aggregation (Han)
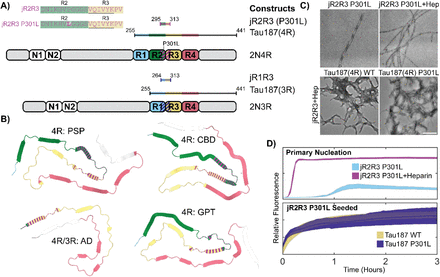 This study explores the spread of tau conformers linked to tauopathies. Using a 19-residue probe peptide with a P301L mutation, researchers found that it forms fibrils capable of inducing aggregation in 4R tau. These fibrils propagate aggregated tau, mirroring the structure seen in 4R tauopathy brain-derived fibrils. Molecular dynamics simulations reveal distinctive features influencing aggregation in 4R tauopathy. N-terminal-flanking residues to PHF6 influence seeding, and a single amino acid change greatly affects seeding capability. The results point to potential isoform-specific therapeutic strategies for treating tauopathies. bioRxiv (2023) This study explores the spread of tau conformers linked to tauopathies. Using a 19-residue probe peptide with a P301L mutation, researchers found that it forms fibrils capable of inducing aggregation in 4R tau. These fibrils propagate aggregated tau, mirroring the structure seen in 4R tauopathy brain-derived fibrils. Molecular dynamics simulations reveal distinctive features influencing aggregation in 4R tauopathy. N-terminal-flanking residues to PHF6 influence seeding, and a single amino acid change greatly affects seeding capability. The results point to potential isoform-specific therapeutic strategies for treating tauopathies. bioRxiv (2023)
|
|
A supramolecular polymer-collagen microparticle slurry for bone regeneration with minimal growth factor (Stupp)
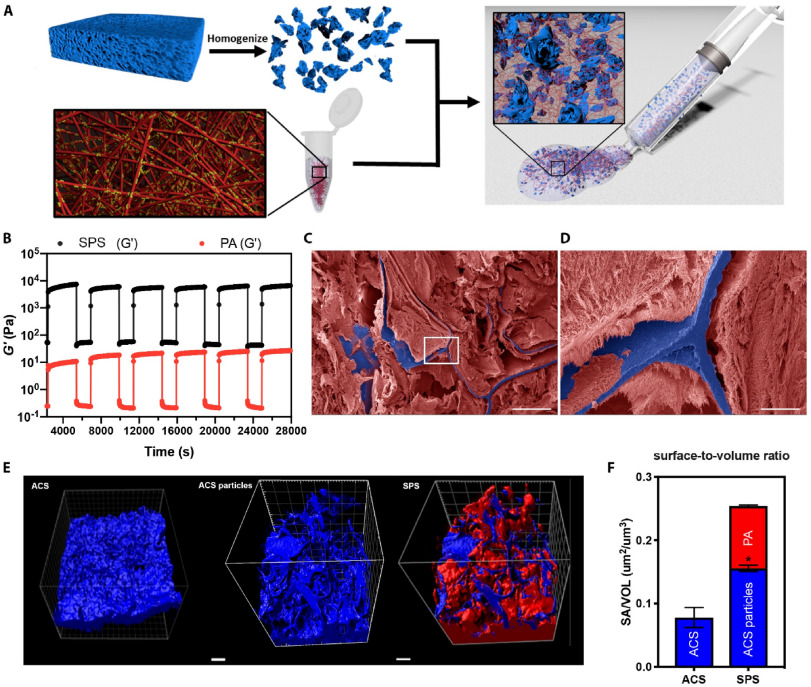 Researchers aimed to enhance bone regeneration using bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) while addressing its high-dose side effects. They devised a novel biomaterial based on a slurry of supramolecular polymer and porous collagen microparticles. This paste transforms into an elastic gel post-implantation, ideal for less invasive procedures. Tested on a rabbit spine fusion model, the biomaterial showcased unprecedented efficacy with ultra-low BMP-2 doses, reducing the growth factor requirement by over 100 times compared to current clinical products. This breakthrough could broaden BMP-2 applications, especially in complex cases necessitating substantial bone formation or for patients with conditions hindering bone regeneration. Biomaterials 302, 122357 (2023) Researchers aimed to enhance bone regeneration using bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) while addressing its high-dose side effects. They devised a novel biomaterial based on a slurry of supramolecular polymer and porous collagen microparticles. This paste transforms into an elastic gel post-implantation, ideal for less invasive procedures. Tested on a rabbit spine fusion model, the biomaterial showcased unprecedented efficacy with ultra-low BMP-2 doses, reducing the growth factor requirement by over 100 times compared to current clinical products. This breakthrough could broaden BMP-2 applications, especially in complex cases necessitating substantial bone formation or for patients with conditions hindering bone regeneration. Biomaterials 302, 122357 (2023)
|
|
Cooperative Carbene Photocatalysis for β-Amino Ester Synthesis (Scheidt)
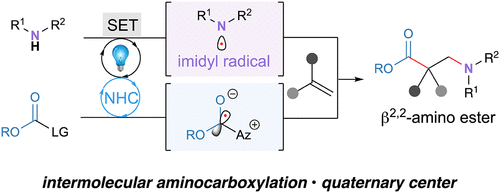 This study tackles the challenge of obtaining β2,2-amino acids crucial for bioactive molecule synthesis. A novel method, using N-heterocyclic carbene/photocatalyzed aminocarboxylation of olefins, was introduced, which ensured high regioselectivity to form β2,2-amino esters. By generating nitrogen-centered radicals from simple imides, selective addition to geminal-disubstituted olefins occurs. Tertiary radicals then cross-couple with a stabilized azolium-based radical, efficiently constructing necessary quaternary centers. Mechanistic studies, including fluorescence quenching experiments, support the proposed catalytic cycle. This advance provides a valuable tool for chemical synthesis and biological investigations involving β2,2-amino acids, which is vital for creating bioactive compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 45, (2023) This study tackles the challenge of obtaining β2,2-amino acids crucial for bioactive molecule synthesis. A novel method, using N-heterocyclic carbene/photocatalyzed aminocarboxylation of olefins, was introduced, which ensured high regioselectivity to form β2,2-amino esters. By generating nitrogen-centered radicals from simple imides, selective addition to geminal-disubstituted olefins occurs. Tertiary radicals then cross-couple with a stabilized azolium-based radical, efficiently constructing necessary quaternary centers. Mechanistic studies, including fluorescence quenching experiments, support the proposed catalytic cycle. This advance provides a valuable tool for chemical synthesis and biological investigations involving β2,2-amino acids, which is vital for creating bioactive compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 45, (2023)
|
|
Investigating the mechanical stability of flexible metal–organic frameworks (Farha)
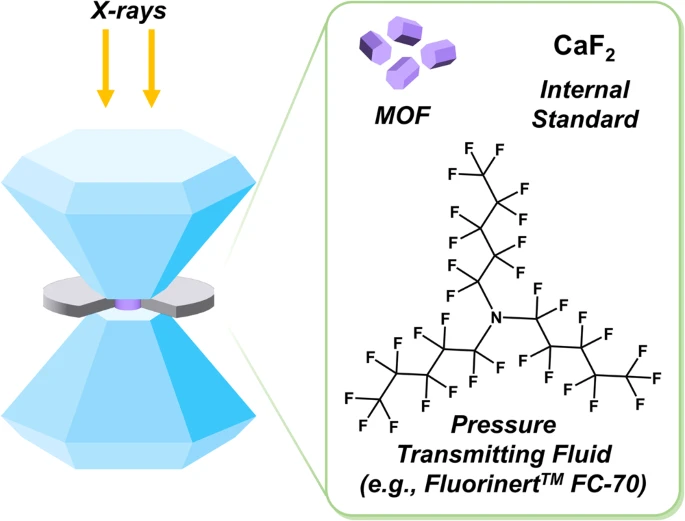 This study explores the mechanical stability of flexible metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) with potential industrial applications. Investigating the compressibility of NU-1400, NU-1401, MIL-88B, MIL-88B-(CH3)2, and MIL-88B-(CH3)4 under pressure, in situ X-ray diffraction reveals a positive correlation between flexibility and bulk moduli. Increased rigidity, influenced by factors like steric hindrance, is found to be detrimental. The research observes reversible unit cell compression, shedding light on factors affecting the mechanical resilience of flexible frameworks. This study lays the foundation for understanding and developing mechanically robust flexible MOFs. Commun Chem 6, 185 (2023) This study explores the mechanical stability of flexible metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) with potential industrial applications. Investigating the compressibility of NU-1400, NU-1401, MIL-88B, MIL-88B-(CH3)2, and MIL-88B-(CH3)4 under pressure, in situ X-ray diffraction reveals a positive correlation between flexibility and bulk moduli. Increased rigidity, influenced by factors like steric hindrance, is found to be detrimental. The research observes reversible unit cell compression, shedding light on factors affecting the mechanical resilience of flexible frameworks. This study lays the foundation for understanding and developing mechanically robust flexible MOFs. Commun Chem 6, 185 (2023)
|
|
Control of Photoswitching Kinetics with Strong Light–Matter Coupling in a Cavity (Kalow)
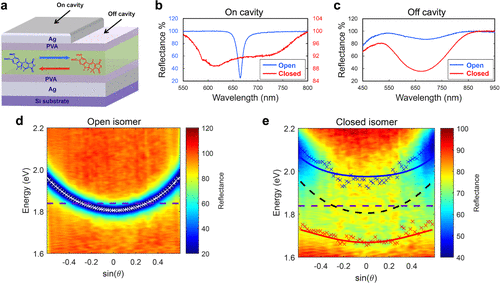 In standard photochemistry, molecules react in their excited states upon absorbing light. However, in strong light-matter coupling, molecules collectively interact with an optical field, forming hybrid states called polaritons. This induces notable changes in excited states, such as delocalized excitations and altered energy levels. While the impact of strong coupling on covalent photochemistry is less explored, this study delves into its effect on photoswitching kinetics within optical cavities. Spiropyran/merocyanine photoswitches exhibit deceleration, while fulgide photoswitches show acceleration under strong coupling. These findings suggest diverse effects on photoswitching kinetics, offering insights into covalent photochemical processes in such environments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 36 (2023) In standard photochemistry, molecules react in their excited states upon absorbing light. However, in strong light-matter coupling, molecules collectively interact with an optical field, forming hybrid states called polaritons. This induces notable changes in excited states, such as delocalized excitations and altered energy levels. While the impact of strong coupling on covalent photochemistry is less explored, this study delves into its effect on photoswitching kinetics within optical cavities. Spiropyran/merocyanine photoswitches exhibit deceleration, while fulgide photoswitches show acceleration under strong coupling. These findings suggest diverse effects on photoswitching kinetics, offering insights into covalent photochemical processes in such environments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 36 (2023)
|


 This study explores the spread of tau conformers linked to tauopathies. Using a 19-residue probe peptide with a P301L mutation, researchers found that it forms fibrils capable of inducing aggregation in 4R tau. These fibrils propagate aggregated tau, mirroring the structure seen in 4R tauopathy brain-derived fibrils. Molecular dynamics simulations reveal distinctive features influencing aggregation in 4R tauopathy. N-terminal-flanking residues to PHF6 influence seeding, and a single amino acid change greatly affects seeding capability. The results point to potential isoform-specific therapeutic strategies for treating tauopathies. bioRxiv (2023)
This study explores the spread of tau conformers linked to tauopathies. Using a 19-residue probe peptide with a P301L mutation, researchers found that it forms fibrils capable of inducing aggregation in 4R tau. These fibrils propagate aggregated tau, mirroring the structure seen in 4R tauopathy brain-derived fibrils. Molecular dynamics simulations reveal distinctive features influencing aggregation in 4R tauopathy. N-terminal-flanking residues to PHF6 influence seeding, and a single amino acid change greatly affects seeding capability. The results point to potential isoform-specific therapeutic strategies for treating tauopathies. bioRxiv (2023) Researchers aimed to enhance bone regeneration using bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) while addressing its high-dose side effects. They devised a novel biomaterial based on a slurry of supramolecular polymer and porous collagen microparticles. This paste transforms into an elastic gel post-implantation, ideal for less invasive procedures. Tested on a rabbit spine fusion model, the biomaterial showcased unprecedented efficacy with ultra-low BMP-2 doses, reducing the growth factor requirement by over 100 times compared to current clinical products. This breakthrough could broaden BMP-2 applications, especially in complex cases necessitating substantial bone formation or for patients with conditions hindering bone regeneration. Biomaterials 302, 122357 (2023)
Researchers aimed to enhance bone regeneration using bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) while addressing its high-dose side effects. They devised a novel biomaterial based on a slurry of supramolecular polymer and porous collagen microparticles. This paste transforms into an elastic gel post-implantation, ideal for less invasive procedures. Tested on a rabbit spine fusion model, the biomaterial showcased unprecedented efficacy with ultra-low BMP-2 doses, reducing the growth factor requirement by over 100 times compared to current clinical products. This breakthrough could broaden BMP-2 applications, especially in complex cases necessitating substantial bone formation or for patients with conditions hindering bone regeneration. Biomaterials 302, 122357 (2023) This study tackles the challenge of obtaining β2,2-amino acids crucial for bioactive molecule synthesis. A novel method, using N-heterocyclic carbene/photocatalyzed aminocarboxylation of olefins, was introduced, which ensured high regioselectivity to form β2,2-amino esters. By generating nitrogen-centered radicals from simple imides, selective addition to geminal-disubstituted olefins occurs. Tertiary radicals then cross-couple with a stabilized azolium-based radical, efficiently constructing necessary quaternary centers. Mechanistic studies, including fluorescence quenching experiments, support the proposed catalytic cycle. This advance provides a valuable tool for chemical synthesis and biological investigations involving β2,2-amino acids, which is vital for creating bioactive compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 45, (2023)
This study tackles the challenge of obtaining β2,2-amino acids crucial for bioactive molecule synthesis. A novel method, using N-heterocyclic carbene/photocatalyzed aminocarboxylation of olefins, was introduced, which ensured high regioselectivity to form β2,2-amino esters. By generating nitrogen-centered radicals from simple imides, selective addition to geminal-disubstituted olefins occurs. Tertiary radicals then cross-couple with a stabilized azolium-based radical, efficiently constructing necessary quaternary centers. Mechanistic studies, including fluorescence quenching experiments, support the proposed catalytic cycle. This advance provides a valuable tool for chemical synthesis and biological investigations involving β2,2-amino acids, which is vital for creating bioactive compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 45, (2023) This study explores the mechanical stability of flexible metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) with potential industrial applications. Investigating the compressibility of NU-1400, NU-1401, MIL-88B, MIL-88B-(CH3)2, and MIL-88B-(CH3)4 under pressure, in situ X-ray diffraction reveals a positive correlation between flexibility and bulk moduli. Increased rigidity, influenced by factors like steric hindrance, is found to be detrimental. The research observes reversible unit cell compression, shedding light on factors affecting the mechanical resilience of flexible frameworks. This study lays the foundation for understanding and developing mechanically robust flexible MOFs. Commun Chem 6, 185 (2023)
This study explores the mechanical stability of flexible metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) with potential industrial applications. Investigating the compressibility of NU-1400, NU-1401, MIL-88B, MIL-88B-(CH3)2, and MIL-88B-(CH3)4 under pressure, in situ X-ray diffraction reveals a positive correlation between flexibility and bulk moduli. Increased rigidity, influenced by factors like steric hindrance, is found to be detrimental. The research observes reversible unit cell compression, shedding light on factors affecting the mechanical resilience of flexible frameworks. This study lays the foundation for understanding and developing mechanically robust flexible MOFs. Commun Chem 6, 185 (2023) In standard photochemistry, molecules react in their excited states upon absorbing light. However, in strong light-matter coupling, molecules collectively interact with an optical field, forming hybrid states called polaritons. This induces notable changes in excited states, such as delocalized excitations and altered energy levels. While the impact of strong coupling on covalent photochemistry is less explored, this study delves into its effect on photoswitching kinetics within optical cavities. Spiropyran/merocyanine photoswitches exhibit deceleration, while fulgide photoswitches show acceleration under strong coupling. These findings suggest diverse effects on photoswitching kinetics, offering insights into covalent photochemical processes in such environments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 36 (2023)
In standard photochemistry, molecules react in their excited states upon absorbing light. However, in strong light-matter coupling, molecules collectively interact with an optical field, forming hybrid states called polaritons. This induces notable changes in excited states, such as delocalized excitations and altered energy levels. While the impact of strong coupling on covalent photochemistry is less explored, this study delves into its effect on photoswitching kinetics within optical cavities. Spiropyran/merocyanine photoswitches exhibit deceleration, while fulgide photoswitches show acceleration under strong coupling. These findings suggest diverse effects on photoswitching kinetics, offering insights into covalent photochemical processes in such environments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 36 (2023)